Java中List遍歷刪除元素remove()的方法
今天碰見根據(jù)條件進行l(wèi)ist遍歷remove的問題,第一時間就是簡單for循環(huán)remove,只知道這么寫不行,不安全,可是為什么呢?你想過嗎?下面就關(guān)于List遍歷remove的問題,深挖一下!
一、幾種常見的遍歷方式
1、普通for循環(huán)
2、高級for循環(huán)

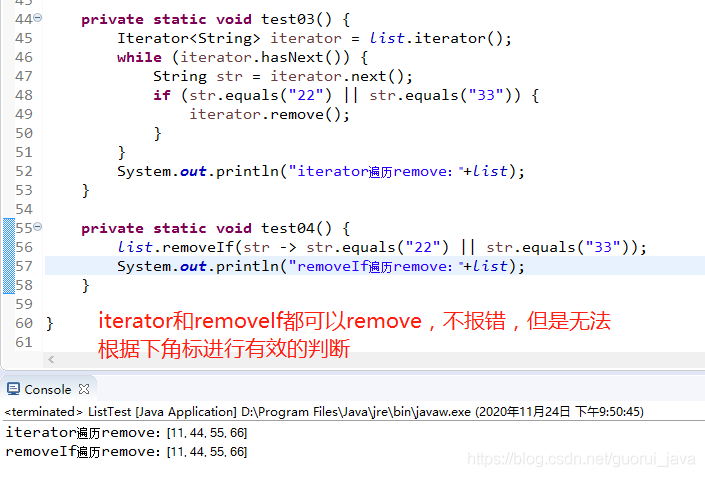
3、iterator和removeIf
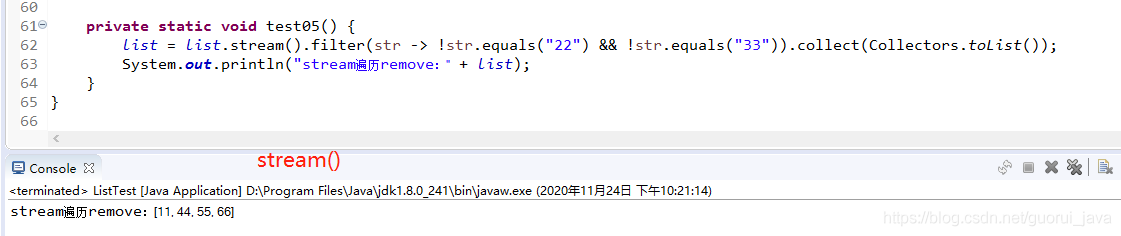
4、stream()
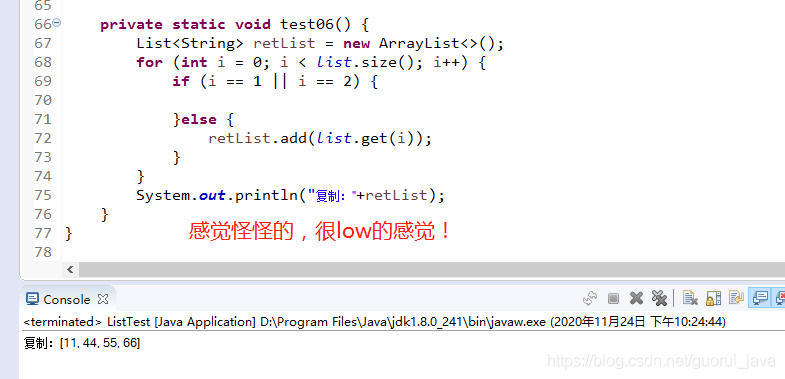
5、復制
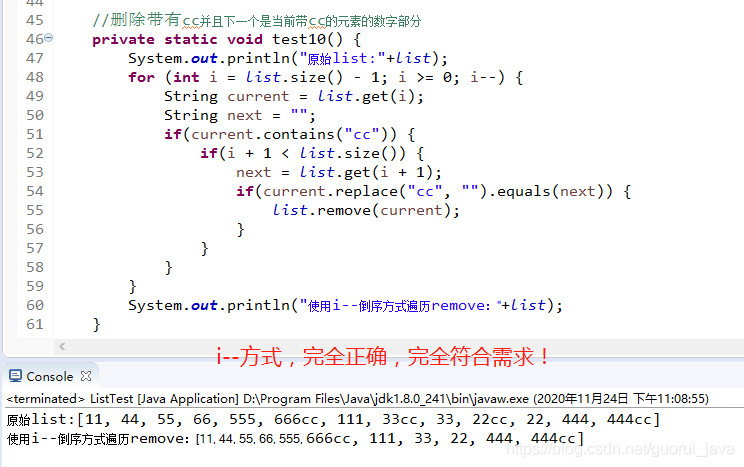
6、普通for循環(huán) --> 倒序方式
二、源碼篇
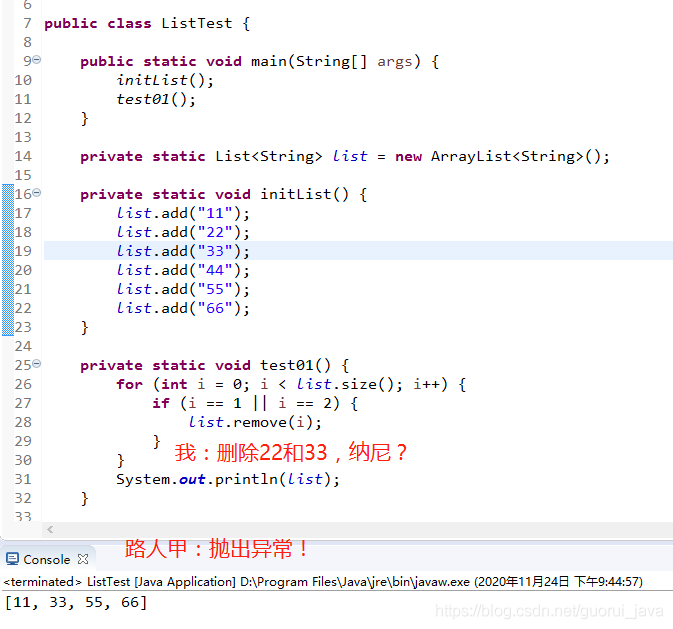
1、普通for循環(huán)出錯原因
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) {fastRemove(index);return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {fastRemove(index);return true; } } return false;}
/* * Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not * return the value removed. */private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) //remove會導致之后的元素往前移動,而下標不改變時就會出現(xiàn)bug System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work}
我們在刪除某個元素后,list的大小發(fā)生了變化,這時候你的的索引也會發(fā)生變化,這時就會導致你在遍歷的時候漏掉某些元素。比如當你刪除第1個元素后,我們?nèi)绻€是繼續(xù)根據(jù)索引訪問第2個元素時,因為刪除的關(guān)系,后面的元素都往前移動了一位,所以實際訪問的是第3個元素。所以這種方式可以用在刪除特定的一個元素時使用,但不適合循環(huán)刪除多個元素時使用。
2、高級for循環(huán)出錯原因
foreach其實是用迭代器來進行遍歷的,而在遍歷時直接使用arraylist的remove方法會導致什么問題呢?
可以再看一下fastremove和迭代器遍歷的內(nèi)部代碼:
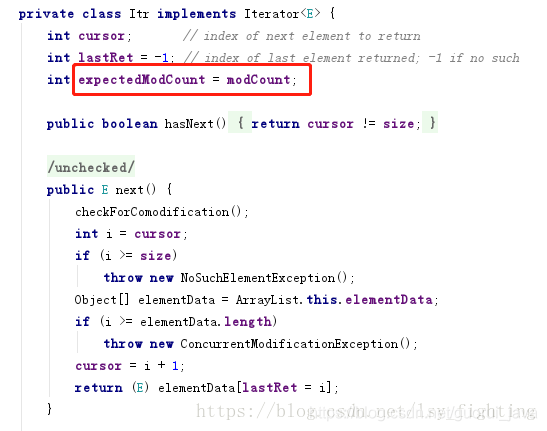
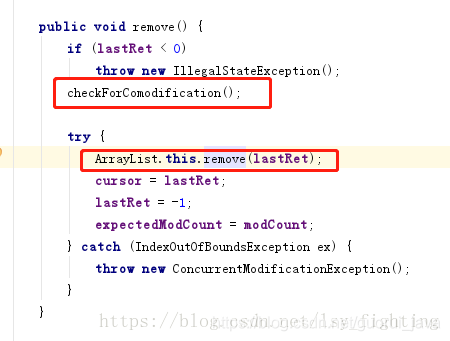
最后導致拋出上面異常的其實就是這個,簡單說,調(diào)用list.remove()方法導致modCount和expectedModCount的值不一致而報異常
final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}//調(diào)用next時會調(diào)用checkForComodification方法檢查 這兩個字段//而fastRemove里面只對modCount 進行了改變 導致拋出異常public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}
所以遍歷時remove并不適用于foreach。
3、java8中新方法removeIf
//內(nèi)部其實就是迭代器遍歷default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); boolean removed = false; final Iterator<E> each = iterator(); while (each.hasNext()) { if (filter.test(each.next())) { each.remove(); removed = true; } } return removed;}
和迭代器差不多,內(nèi)部實現(xiàn)也是迭代器。
三、總結(jié)
1、在不考慮內(nèi)存大小會不會出現(xiàn)OOM的時候,采取復制一個新的list的方法速度更快,適用于集合中對象不算多的時候,畢竟只需要add操作。
2、當集合中元素過多時,復制list就顯得有些笨重了,采用迭代器的方式進行遍歷較快一些,并且不用關(guān)注小角標的變化。
3、不考慮性能的時候使用removeIf方法,代碼簡潔明了。
4、當要針對角標進行元素的remove時,使用倒序遍歷的方式最為妥當。
到此這篇關(guān)于Java中List遍歷刪除元素remove()的方法的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java List遍歷刪除元素內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 如何用 Python 制作一個迷宮游戲2. 部署vue+Springboot前后端分離項目的步驟實現(xiàn)3. vue組件庫的在線主題編輯器的實現(xiàn)思路4. Django如何使用asyncio協(xié)程和ThreadPoolExecutor多線程5. idea設(shè)置自動導入依賴的方法步驟6. 網(wǎng)頁中img圖片使用css實現(xiàn)等比例自動縮放不變形(代碼已測試)7. PHP程序處理網(wǎng)頁表單的GET和POST方法另外用法8. JavaScript實現(xiàn)組件化和模塊化方法詳解9. ASP.NET MVC通過勾選checkbox更改select的內(nèi)容10. PHP的類--功能齊全的發(fā)送郵件類
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備